Search
Now showing items 1-10 of 33
Aufsatz
 S-Adenosyl-L-Homocysteine Hydrolase Inhibition by a Synthetic Nicotinamide Cofactor Biomimetic
S-Adenosyl-L-Homocysteine Hydrolase Inhibition by a Synthetic Nicotinamide Cofactor Biomimetic
(2018-03-21)
S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine (SAH) hydrolases (SAHases) are involved in the regulation of methylation reactions in many organisms and are thus crucial for numerous cellular functions. Consequently, their dysregulation is associated with severe health problems. The SAHase-catalyzed reaction is reversible and both directions depend on the redox activity of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) as a cofactor. Therefore, nicotinamide cofactor biomimetics (NCB) are a promising tool to modulate SAHase activity. In the ...
Dissertation
 Identifizierung und funktionelle Charakterisierung neuer A-Kinase-Ankerproteine (AKAPs) im Modellorganismus C. elegans
Identifizierung und funktionelle Charakterisierung neuer A-Kinase-Ankerproteine (AKAPs) im Modellorganismus C. elegans
(2012-05-07)
In dieser Arbeit sollten neue Interaktionspartner der regulatorischen Untereinheit (R-UE) der Proteinkinase A (PKA) und des Modellorganismus C. elegans identifiziert und funktionell charakterisiert werden. Im Gegensatz zu Säugern (vier Isoformen), exprimiert der Nematode nur eine PKA-R-Isoform. Mittels in silico Analysen und so genannten „Pulldown“ Experimenten, wurde insbesondere nach A Kinase Ankerproteinen (AKAP) in C. elegans gesucht. Aus in silico Recherchen resultiert das rgs5 Protein als mögliches Funktionshomolog ...
Dissertation
 Identifizierung und Optimierung von Biomarkern der Karzinogenese des duktalen Pankreaskarzinoms, des Kolonkarzinoms und des Prostatakarzinoms
Identifizierung und Optimierung von Biomarkern der Karzinogenese des duktalen Pankreaskarzinoms, des Kolonkarzinoms und des Prostatakarzinoms
(2008-04-28)
Die Erforschung der Biologie maligner Tumoren beschränkte sich über lange Zeit auf die Suche nach genetischen Veränderungen. Dies hat sich in den letzten Jahren grundlegend geändert, da sich aus dem Wissen um die molekularen Veränderungen in den frühesten histomorphologisch erkennbaren Vorläuferläsionen neue Möglichkeiten zur Früherkennung und Prävention maligner Tumoren ergeben. Darüber hinaus gewinnen Aspekte zur Aufklärung des Krebs- und Progressionsrisikos zunehmend an Bedeutung. Voraussetzung für die Beantwortung ...
Dissertation
 Analyse von Protein-Ligand Interaktionen zur Charakterisierung zyklonukleotidbindender Proteine
Analyse von Protein-Ligand Interaktionen zur Charakterisierung zyklonukleotidbindender Proteine
(2014-04-10)
Hyperpolarisations-aktivierte zyklonukleotid-gesteuerte (HCN) Kanäle übernehmen wichtige Funktionen in der Regulation der Herz- und Neuronalaktivität und können über einen dualen Mechanismus aus Membranhyperpolarisation und der Bindung von zyklischen Nukleotiden aktiviert werden. Ein großes Ziel der aktuellen Forschung ist die Entwicklung neuartiger Inhibitoren, die einer Fehlregulation der Kanäle entgegenwirken. In der vorliegenden Arbeit wurde die Regulation von HCN Kanälen durch zyklische Nukleotide im Detail ...
Dissertation
 Untersuchung zum Phosphorylierungsstatus der katalytischen Untereinheit der PKA mittels proteomischer Techniken
Untersuchung zum Phosphorylierungsstatus der katalytischen Untereinheit der PKA mittels proteomischer Techniken
(2011-11-16)
ZUSAMMENFASSUNG: Das Phosphorylierungsmuster eines Proteins ist kein statischer Zustand, sondern vielmehr ein dynamischer Status, den es in der modernen funktionellen (Phospho-) Proteomik und Analytik abzubilden gilt. Klassischerweise erfolgt der Nachweis der Proteinphosphorylierung auf Peptid-Ebene mittels MS/MS Sequenzierung. Diese Standardmethode der shotgun Phosphoproteomanalytik vernachlässigt jedoch wegen den in LC MS/MS Analysen oftmals schwer detektierbaren Phosphopeptiden gerade den variablen und oftmals nur ...
Dissertation
 Biochemische und Zellbiologische Charakterisierung der humanen Proteinkinase X
Biochemische und Zellbiologische Charakterisierung der humanen Proteinkinase X
(2009-10-16)
Diese Dissertation befasst sich mit der Charakterisierung der humanen Proteinkinase (PRKX) mittels zellbiologischer (rekombinante Expression in Baculovirus, endogenes Protein, BRET) wie auch biochemischer Elemente (Aktivitaetsassays, Biacore). Dabei wurde die humane PRKX mit den Drosophila- und Maus-Isoformen DC2 und PKARE verglichen, wie auch putative Phosphorylierungsstellen durch andere Kinasen identifiziert, welche einen Einfluss auf Interaktion und Lokalisation des Enzyms haben koennten.
Dissertation
 Regulation und Koordination der Proteinkinase A im cAMP-vermittelten Signalweg
Regulation und Koordination der Proteinkinase A im cAMP-vermittelten Signalweg
(2011-05-11)
Die cAMP-abhängige Proteinkinase ist an der Regulation grundlegender zellulärer Prozesse, wie Entwicklung und Differenzierung, sowie Stoffwechselprozessen, beteiligt. Das Holoenzym bestehend aus einem Dimer regulatorischer (R) und zwei katalytischer C (C) Untereinheiten wird durch den sekundären Botenstoff cAMP reguliert. Die molekulare Grundlage der Holoenzymdynamik, sowie die räumliche und zeitliche Koordination der Holoenzyme in der cAMP-vermittelten Signaltransduktion sind zentrale Themen der aktuellen Forschung. ...
Dissertation
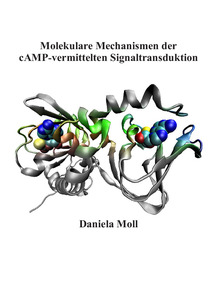
 Molekulare Mechanismen der cAMP-vermittelten Signaltransduktion
Molekulare Mechanismen der cAMP-vermittelten Signaltransduktion
(Universität Kassel, Abteilung Biochemie, 2007-05)
Zusammenfassung - Der sekundäre Botenstoff zyklisches Adenosinmonophosphat (cAMP) reguliert viele fundamentale zelluläre Prozesse wie Zellproliferation, Differenzierung, Energiemetabolismus und Genexpression. In eukaryotischen Zellen vermittelt die cAMP-abhängige Proteinkinase (PKA) die meisten biologischen Funktionen von cAMP. Die PKA besteht aus jeweils zwei regulatorischen (R) und katalytischen (C) Untereinheiten, die zusammen einen inaktiven Holoenzymkomplex bilden, der durch cAMP aktiviert wird.
In dieser ...